CHRIST University offers rigorous programs, valuable resources, and countless opportunities that will enable you to pursue your desired course of study..

The programmes offer deep insight into the built environment through ecological, social, artistic, and technological lenses.
Explore

The School of Commerce, Finance and Accountancy is dedicated to fostering academic excellence and holistic development
Explore
The School of Education offers quality teacher education with a focus on research and social responsibility.
Explore
Offers a wide range of programmes approved by the University Grants Commission (UGC) and All India Council for Technical Education
Explore
The school explores inquiry beyond words through history, philosophy, critical and cultural studies.
Explore
School of Law, Christ University offers quality legal education with a focus on ethics, justice, and practical training.
Explore
The programs foster scientific insight, ethical awareness, and skills for practice, research, and critical thinking.
Explore
Offers UG to post-doctoral programs in Chemistry, Physics, Math, Life Sciences, and Computing Explore

Dedicated to interdisciplinary learning, engaging students and faculty in a variety of cross-disciplinary experiences and programs
... Explore
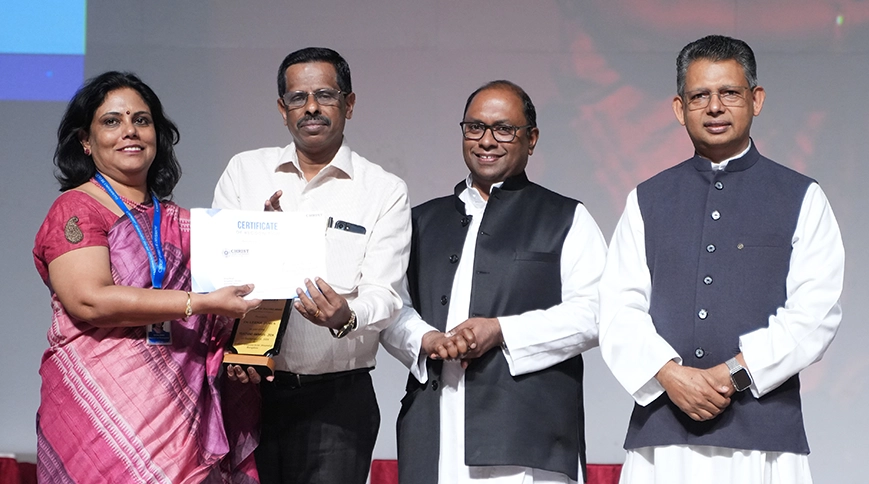

Dr Leena James, School of Business Management and Head of the SDG Cell, has been conferred with the prestigious Women Change Maker of the Year Award at the New Age Summit - Business and Education Conference.
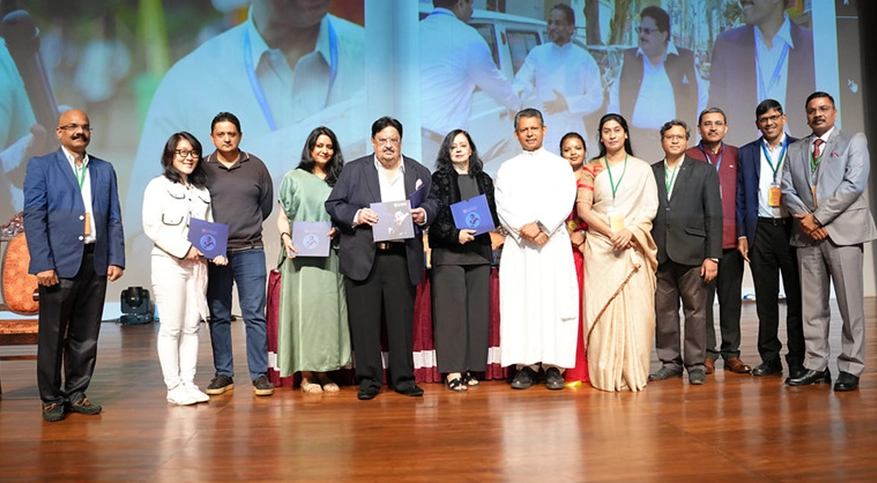

Dr. Fr Joseph C C, Vice Chancellor
Distinguished Service Award during the 55th Annual Family Day 2025 - “A Day to Reunite, Reflect, and Reignite”
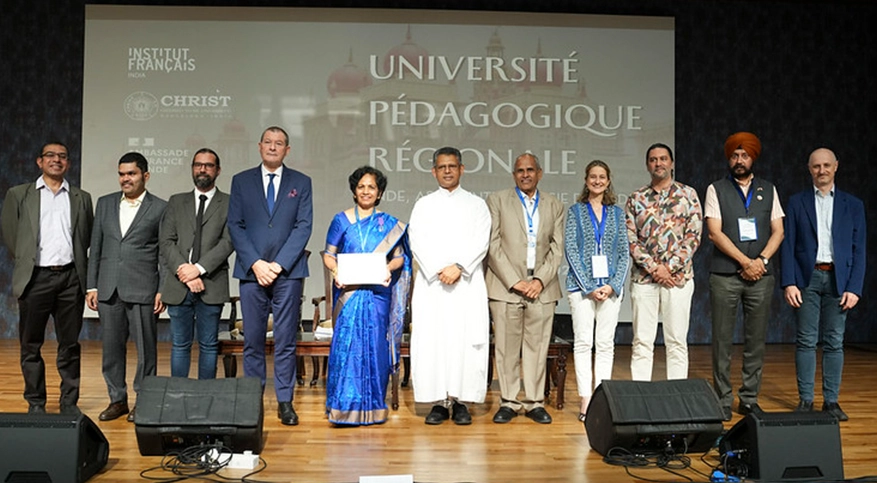

Conferral of the French Decoration, the "Ordre des Palmes Académiques" (Order of Academic Palms) to Dr Mallika Krishnaswami by Consul General of France Marc Lamy, Bangalore.
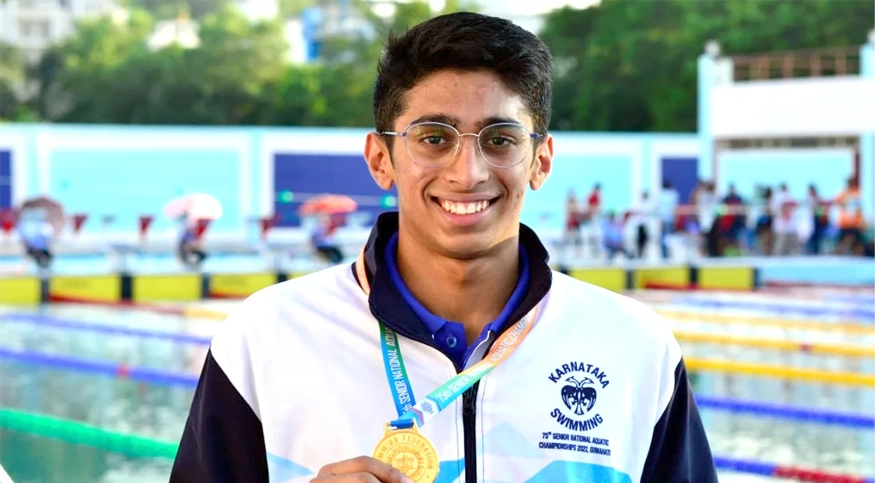

The Karnataka Swimming Association proudly congratulates Aneesh S Gowda on receiving the prestigious KOA Award for the year 2023 | Felicitated with SSI KARNA Award by Sports Science India in Kalinga stadium by Shri Kanak Vardhan Singh, Deputy Chief Minister of Odisha.
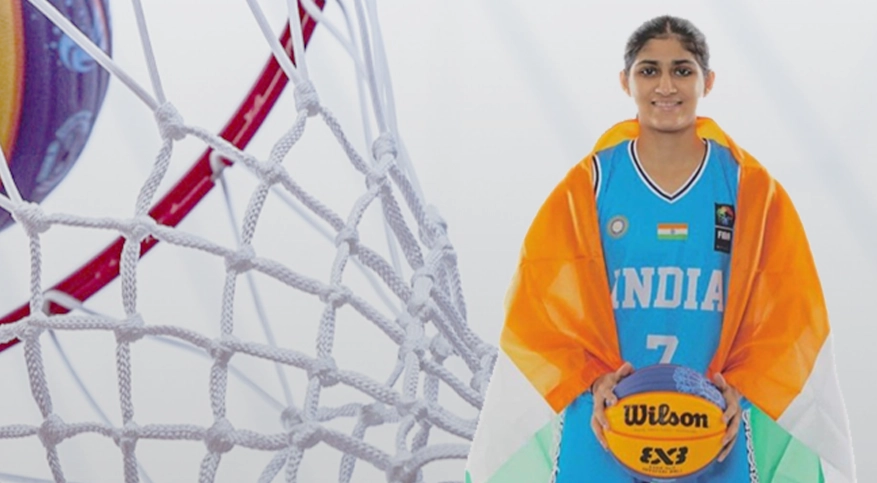

Gunjan Mantri (I BA) was selected to represent INDIA in the Under-18 Women’s National Basketball.
Team in Dubai from 11th to 18th November 2024.

Ms.Sarah Lourdes Pais and Ms.Bishalta Pradhan from 6 EMS have bagged "British Council 70th Anniversary Scholarship" worth $10,620 to pursue Master's Degree in Data Science at Liverpool Hope University.
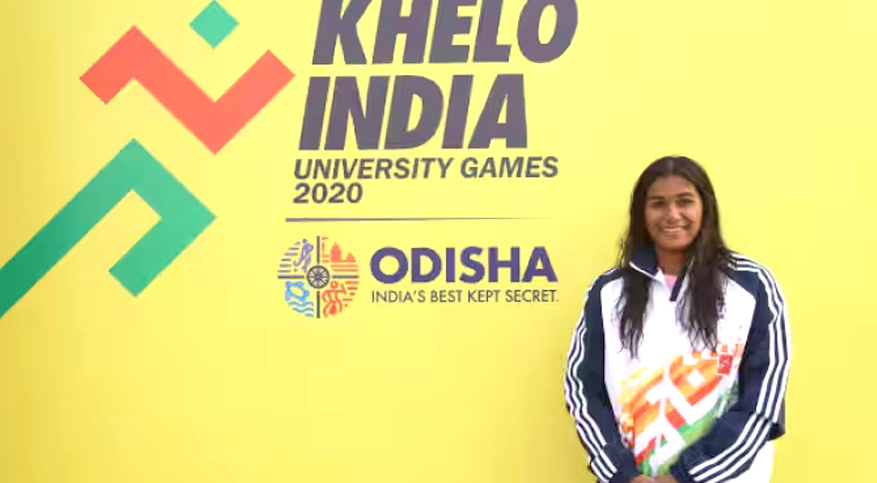

RIDDHI S BOHRA of II BBA won a silver medal in the 50M BREASTSTROKE & bronze medal in the 100 breaststrokes the 1st KHELO INDIA UNIVERSITY GAMES held at KIT- Bhuvaneshwar, ODISHA

Christ University Wins Excellence in Tech-Enhanced Training and Placement Award at TechEDU India Awards 2025.

CHRIST (Deemed to be University) Awarded ‘Outstanding Private Deemed to be University’ at The Economic Times Education Excellence Awards 2025
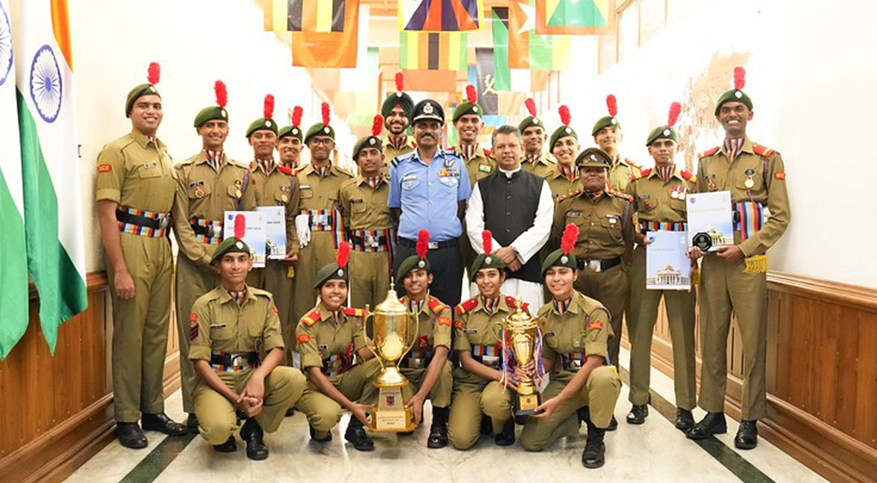

CHRIST University's NCC bags the prestigious "Best Institution Award" from the Karnataka and Goa Directorate for the year 2024-25
Students receiving Deputy Director General's Commendation from Air Cmde SB Arun Kumar VSM, Deputy Director General, NCC Karnataka & Goa Directorate

Physical Sciences: Christ University is ranked between 601 and 800 globally
Physical Sciences is a group of subjects such as mathematics and statistics, physics and astronomy, chemistry, geology, environmental sciences, and earth-marine sciences.

The University welcomes students from all over the world to a vibrant environment of religious and racial harmony, secularism and cultural diversity Know more
Christ University hosts distinguished guests from academia, industry, and the arts, inspiring students and faculty through insightful interactions and discussions.


Padma Bhushan | Padma Vibhushan | Bharat Ratna
Former President of India | Indian Aerospace Scientist

Bharat Ratna | Padma Vibhushan
Former President of India

Awarded the Nobel Peace Prize
Spiritual Leader of Tibetan Buddhism

Padma Vibhushan | Indira Gandhi Paryavaran Puraskar
Indian Spiritual Guru and Founder of the Isha Foundation
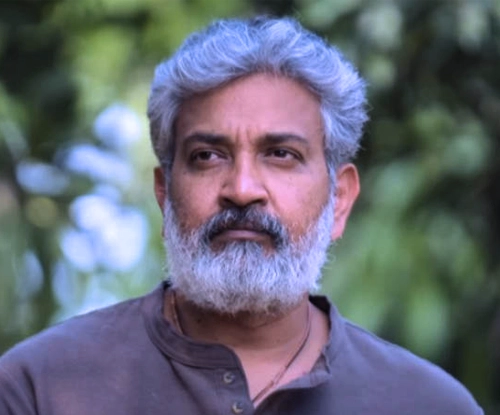

Padma Shri
Indian Filmmaker

Padma Bhushan | Padma Vibhushan
Indian Space scientist | Former Chairman, Indian Space Research Organisation
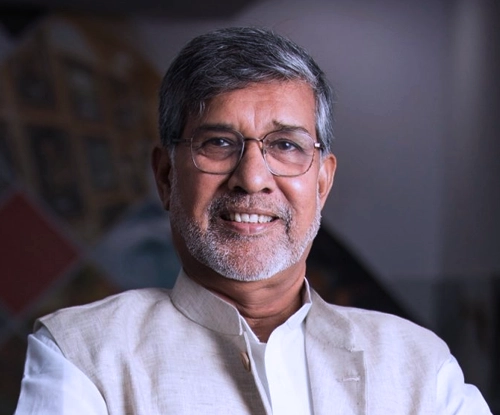

Nobel Peace Laureate
Indian Social Reformer
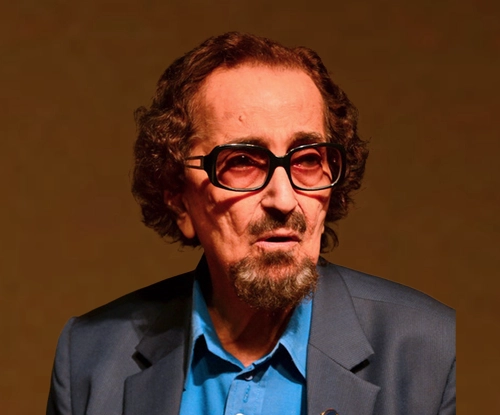

Conferred with Padma Shri
Indian Theatre Personality and Ad Film Maker
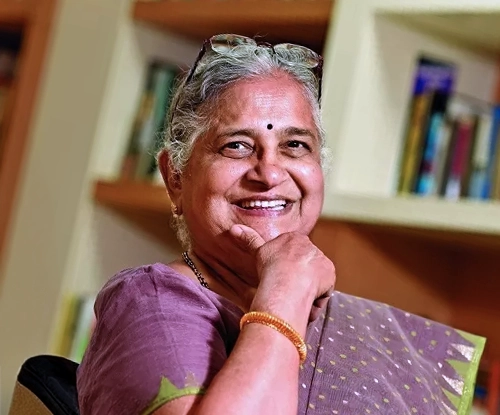
Awarded the Padma Bhushan
Indian Educator, Author, and Philanthropist | Former Chairperson, Infosys Foundation
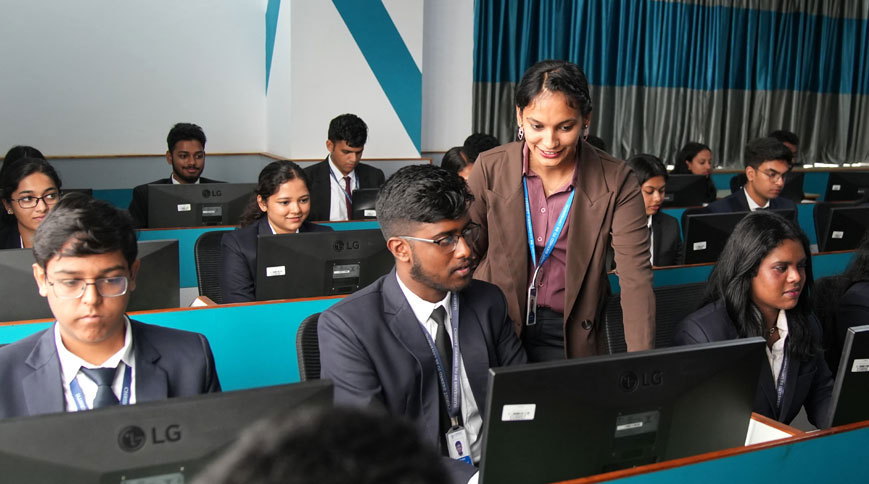

There are multiple labs affiliated to Schools on each campus of CHRIST. There are science labs, computer labs, engineering labs, language labs, performances studios, Media labs, incubation and innovation Centres to fortify the research culture.

Industrialist
Bachelor of Commerce (BCom)
1972

Indian Police Service
PCMB (Christ College) 1996

Chairman & CEO
Tharanco Group
Bachelor of Commerce (BCom - 1982)

IAS
Indian Administrative Service
BSc CME (2006)

Executive Director
EY
Bachelor of Commerce (BCom - 2005)

Legal Officer
Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
The Hague
School of Law

Indian Actor
Film Industry
BA Communication and Media, English and Psychology (CEP - 2012)

Lawyer
Bradley Allen Love Lawyers, Canberra, Australia
School of Law

Co-founder
Kompany Hospitality & Soka
Bachelor of Hotel Management (2004-08)

SVP and Managing Director (India)
Blume Global
Bachelor of Commerce (BCom - 1989)

Managing Director
Canadian International School Bangalore
Bachelor of Business Management (BBM - (2004)

Indian Actress
Tamil/Malayalam
Bachelor of Commerce Tourism (2013)

Musician
Director, Taaqademy
BA JPEnglish (1998)

Managing Director
Shand Group of Industries
Bachelor of Commerce (BCom - 1989)

Co-Founder & CMO,
Camcom
Bachelor of Hotel Management (1992 - 95)

Chairman and Managing Director
White Group
BSc PCM (1987)

Politician
MLA, Byatarayanapura Constituency, Bangalore
Bachelor of Business Management (BBM - 1994)

Professor & Principal
Apeejay Institute of Hospitality, Navi Mumbai
Bachelor of Hotel Management (1991 - 94)

Indian Actress / Producer (Kannada)
Film Industry
Bachelor of Business Management (BBM)
(2009)

Indian Actress / Model (Kannada)
Film Industry
BA Communication and Media, English and Psychology (CEP - 2012)

Senior Vice President
Masai School
Bachelor of Business Management (BBM - 1995)

Vice President
JP Morgan
Master in Business Administration (MBA - 2008)

Executive Editor - News
Republic TV
BA JPEnglish (2007)

Business Editor
Deccan Herald
BA JPEnglish (2006)

Restauranteur
Director, Empire Group of Restaurants
Bachelor of Hotel Management (BHM - 2014)

KAS
Karnataka Administratice Service (KAS)
Bachelor of Commerce (BCom - 2016)

Indian Actor
Film Industry
Bachelor of Business Management (BBM - 1997)

Partner
P N RAO FINE SUITS
Bachelor of Business Management (BBM - 2001)

Advocate, Supreme Court of India
Legal Consultant, Ministry of External Affairs
Bachelor of Commerce (BCom - 2007)

Exective Chef
Taj Hotels Resorts and Palaces
Bachelor of Hotel Management (BHM - 1999)

Politician and Lawyer
National Vice President, Bharatiya Janata Yuva Morcha
BA LLB (2011)

Politician
Member of Legislative Assembly Mandar Constituency
Bachelor of Business Administrtaion (BBA - 2010)

Film Director
Documentary Maker and Theater Person
BA Communication and Media, English and Psychology (CEP - 1994)

IAS
Indian Administrative Service
Master of Business Administration (MBA - 2009)

Senior Vice President
Bank of America
Master of Computer Applications (MCA - 2000)

Vice President
Goldman Sachs
BCom (2011)

IAS
Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
PGDM

Indian Politician
Member of Parliament, Kottayam | Former, Loksabha MP, Idukki

Indian Police Service (IPS)
Former Commissioner of Police
Bangalore City

IPS
Indian Police Service (IPS)
BCom

President
The Narayana Group
BCom

Playback Singer
South Indian Films
BSc CMS (2006)

Maharani of Mysore
Wife of Yaduveer Krishnadatta Chamaraja Wadiyar, 27th Maharaja (King) of Mysore
MA Economics

Radio Jockey
94.3 Radio One
BA CEP (2014)

Senior Vice President
JP Morgan Chase & Co
(2001)

IPS
Indian Police Service (IPS)
MBA (2006)

Second in Command
Central Reserve Police Force
Chennai
BA HEP (1999)

CEO, Vee Technologies
Vice Chairman, Sona Group of Instituions
BCom (1988)

Executive Chef
Sheraton Grand Bangalore
BHM

Executive Director
Cadabams Group
BA (Psychology, Communicative English, Literature)
MSc Clinical Psychology (2005 - 2010)

Managing Director
Cleanslate Communications, London - United Kingdom
BBM (1994-1997)

Director
Marketing at Hitachi Vantara, India & SAARC
School of Business and Management, MBA, Marketing (1996)



| NURTURING EXCELLENCE
| ENRICHING LIVES
| TRANSFORMING FUTURE
Socialize
with wide Numbers